Volumes
Overview
Volumes are file systems (local or remote). They can be used for app data storage or mounted into apps as a way to share files.
Volumes can be added from the Volumes view:
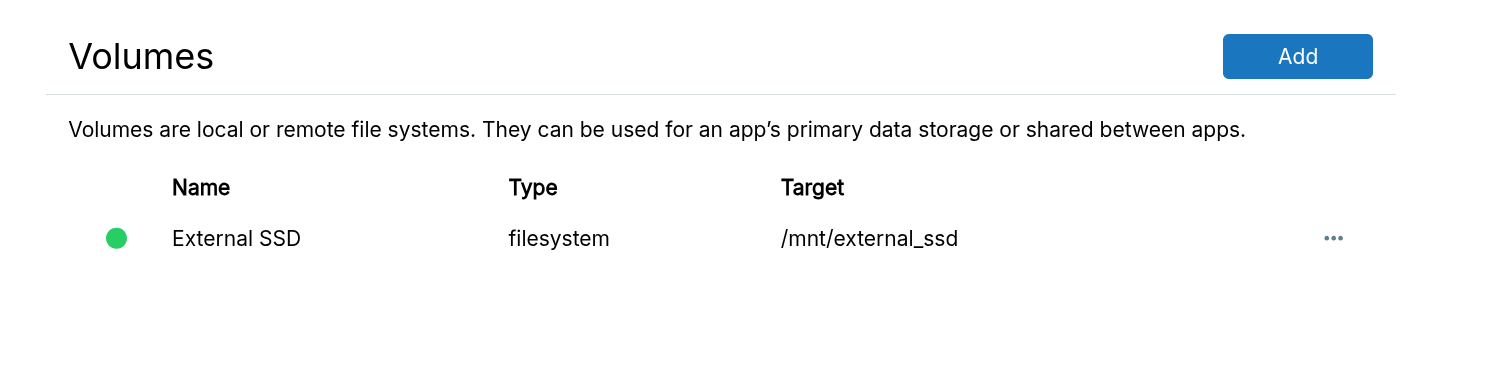
The volume can be set as the data directory or mounted into an app in the app's Mounts section:
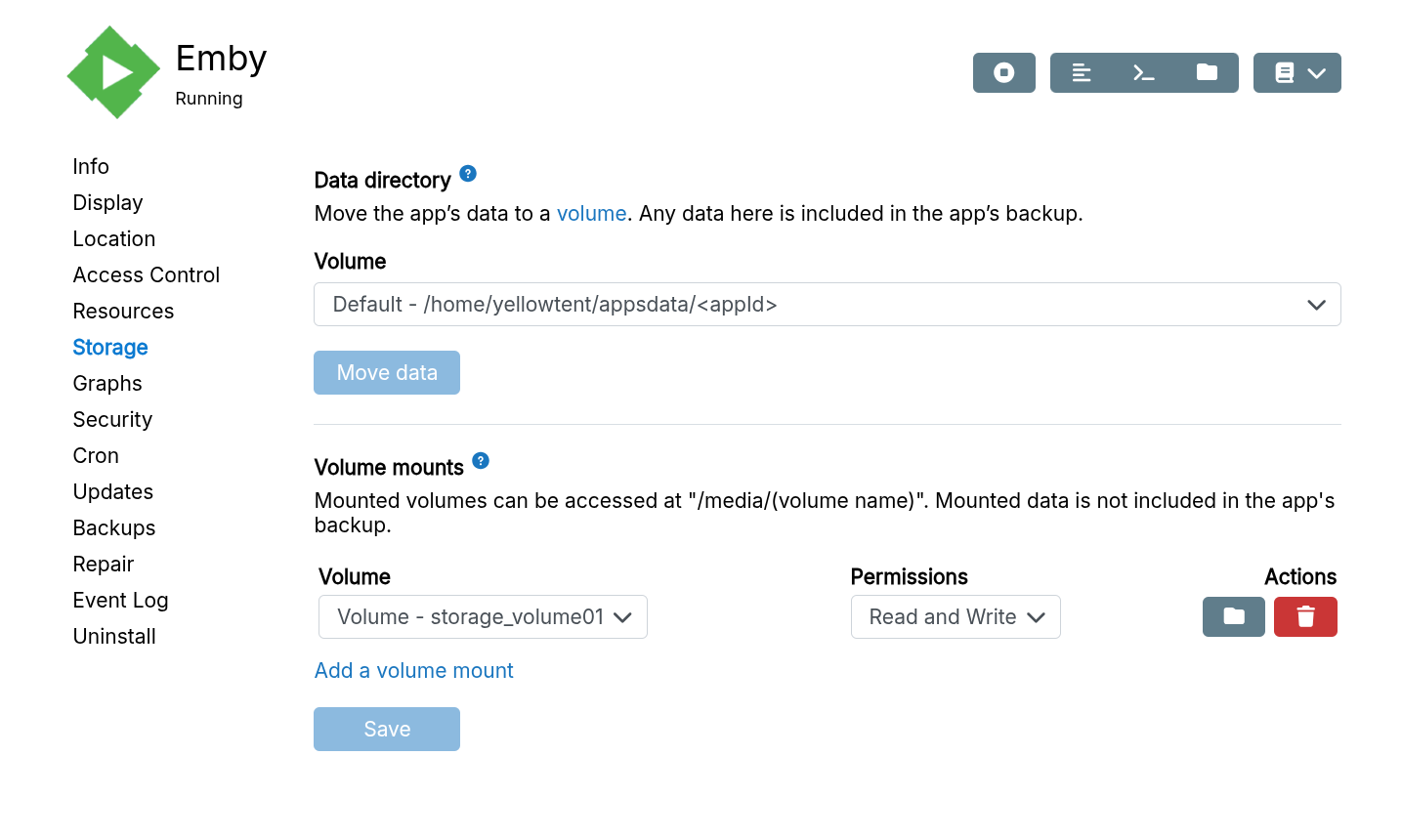
Volumes used as app mounts are not included in backups. Back up mounted volume data separately if needed.
Mount type
Volumes are mounted automatically on server startup via systemd under /mnt/volumes.
If you want to set up a custom fstab entry or custom systemd mount, use the Filesystem (mountpoint) type.
CIFS
CIFS mounts CIFS shares. CIFS lacks user and group support. This makes it unsuitable for app data directories.
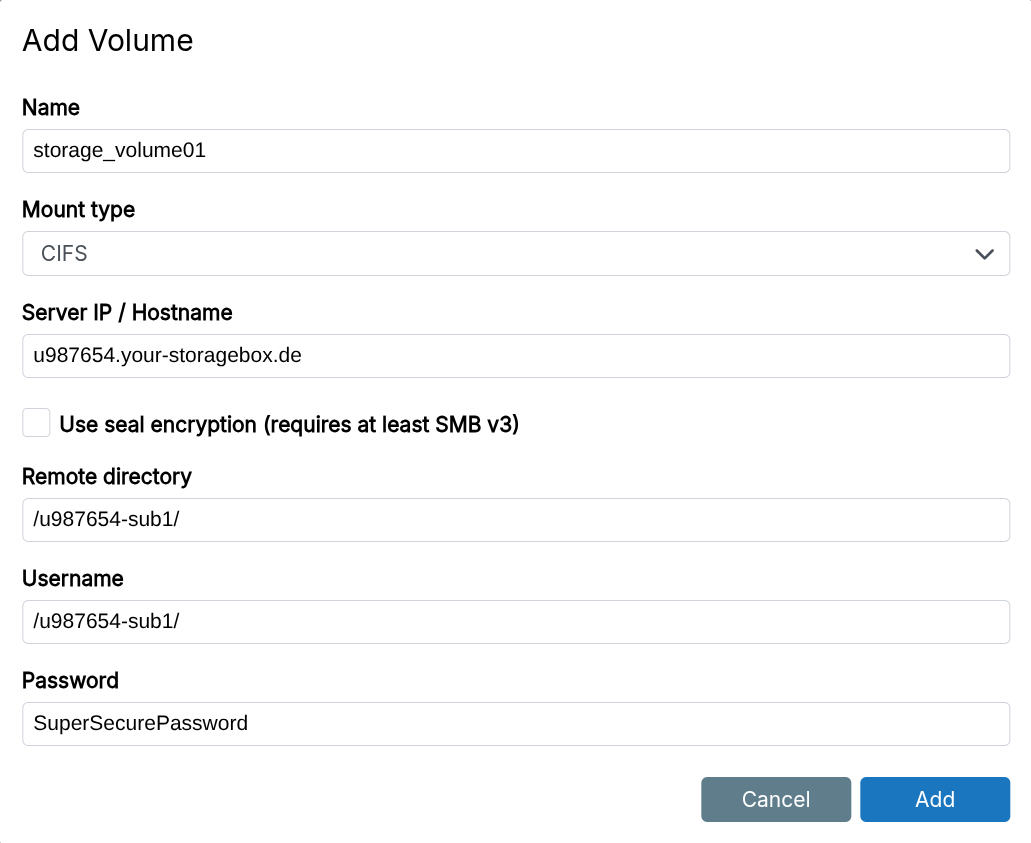
For Hetzner Storage Box, use /backup as the Remote Directory for the main account, or /subaccount for sub accounts.
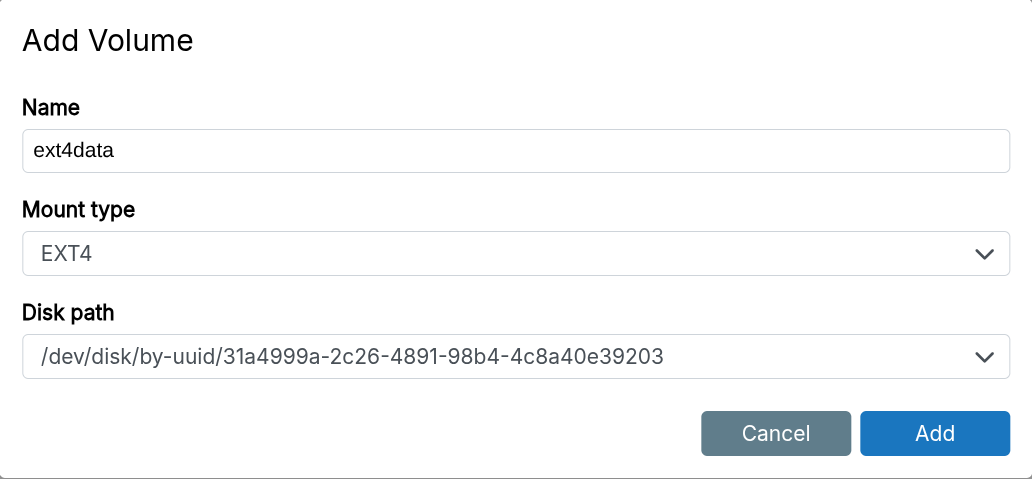
EXT4
The EXT4 type mounts EXT4 disks.
Use blkid or lsblk to get the disk's UUID.
Filesystem
Apps run sandboxed and do not have access to the host filesystem. The Filesystem type can be used to give apps access to arbitrary directories.
Apps run as different users depending on the packaging. chmod 777 permission is recommended for maximum app compatibility.
As a security measure, only host paths under /mnt, /media, /srv and /opt are allowed.
Filesystem (mountpoint)
The mountpoint type is similar to filesystem. The specified path is verified to be mounted before apps are started.
As a security measure, only mount points under /mnt, /media, /srv and /opt are allowed.
NFS
NFS mounts NFSv4 shares from an NFS server. See this guide for NFS server setup.
By default, NFS maps root to nobody for security (prevents setuid files). Add no_root_squash to the NFS server's exports file to disable this.
NFS traffic is unencrypted and can be tampered. Use NFS mounts only on secure private networks.
SSHFS
SSHFS mounts file systems over SSH (using SFTP).
SSHFS volumes cannot be used as an app's data directory.
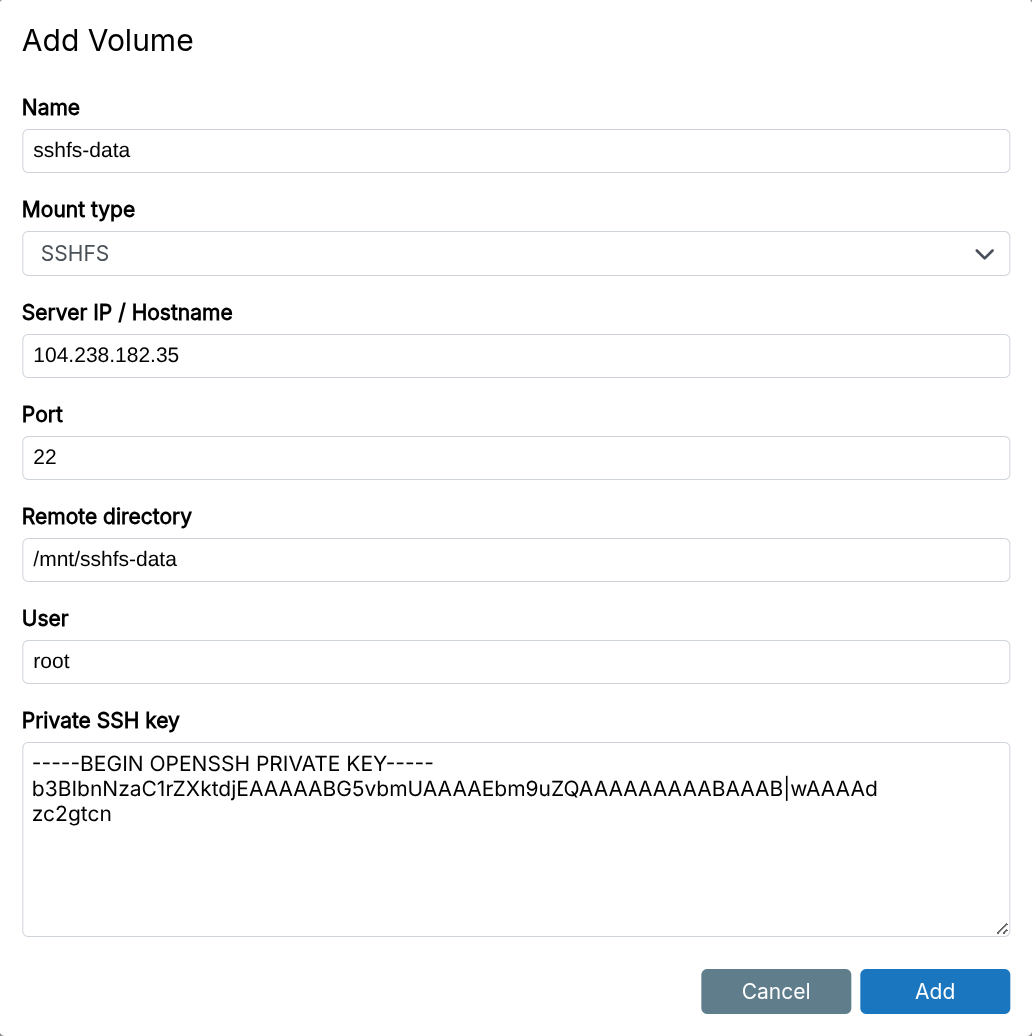
For Hetzner Storage Box, use /home as the Remote Directory (or leave empty). Sub accounts may be unreliable with SSHFS. Use CIFS instead.
XFS
XFS mounts external XFS disks.
Use blkid or lsblk to get the disk's UUID.
Remount
The current mount status is shown to the left. A green icon indicates a successful mount. A red icon indicates
there is some problem. Use the Remount action to attempt a remount.

File manager
The File Manager provides browser-based access to the volume:

Sharing
Sharing volumes across apps requires careful permission configuration because apps run as different users.
The media group enables cross-app file access. This group includes www-data (UID 33) and cloudron (UID 1000), which most apps use.
To prepare a volume for sharing:
-
Identify the mount directory:
/mnt/volumes/<volume-id>for non-filesystem volumes, or the host path for filesystem volumes. -
Run the following commands:
root@my:/# export MOUNT_DIR=/path/to/the/mount/directory
root@my:/# chmod 777 $MOUNT_DIR
root@my:/# chgrp media $MOUNT_DIR
root@my:/# chmod g+s $MOUNT_DIR
root@my:/# setfacl -d -m g::rwx $MOUNT_DIR
root@my:/# setfacl -d -m o::rx $MOUNT_DIR
These commands ensure new files are automatically owned by the media group. Verify the configuration:
root@my:/# touch $MOUNT_DIR/test-file
root@my:/# ls -l $MOUNT_DIR/test-file
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root media 0 Nov 3 22:41 /../test-file
New files now have correct permissions for media group access.