Certificates
Overview
Cloudron integrates with Let's Encrypt to install certificates for apps. Certificates are renewed automatically.
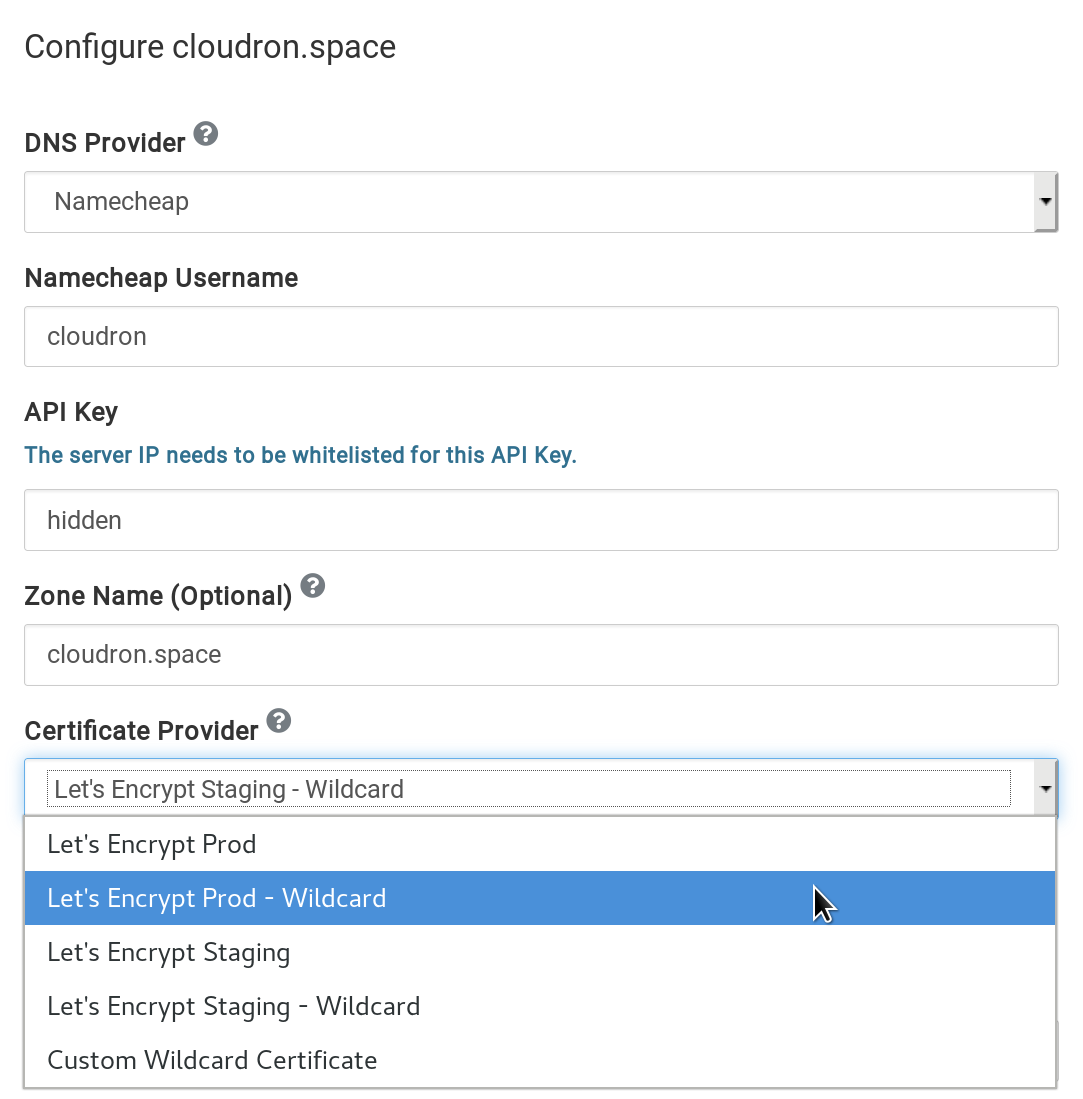
Certificate Providers
Cloudron supports the following certificate providers:
Let's Encrypt Prod- Obtain individual certs for each domain. This provider uses HTTP automation and requires inbound port 80 to be open. This provider will list your individual domain names in the Certificate transparency project.Let's Encrypt Prod - Wildcard(default) - Obtain wildcard certs for each domain. This provider uses DNS automation and can only be used with programmatic DNS API providers.Let's Encrypt Staging- Obtain individual certs for each domain from Let's Encrypt staging endpoint. These certs are for testing and not trusted by the browser. This provider uses HTTP automation and requires inbound port 80 to be open.Let's Encrypt Staging - Wildcard- Obtain wildcard certs for each domain from Let's Encrypt staging endpoint. These certs are for testing and not trusted by the browser. This provider uses DNS automation and can only be used with programmatic DNS API providers.Self-Signed/Custom Certificate- Disable Let's Encrypt integration and use a custom wildcard certificate instead.
Certificate provider can be set per-domain from the Domains view under the domain's Advanced settings.
Custom certificates
Wildcard certificate
A custom wildcard certificate can be provided per domain in advanced settings of a domain in the
Domains view. When setting such a certificate, make sure to add both the bare domain and the
wildcard domain as part of the certificate.
Follow this tutorial for instructions on how to generate a custom wildcard certificate that has both the bare domain and the wildcard domain.
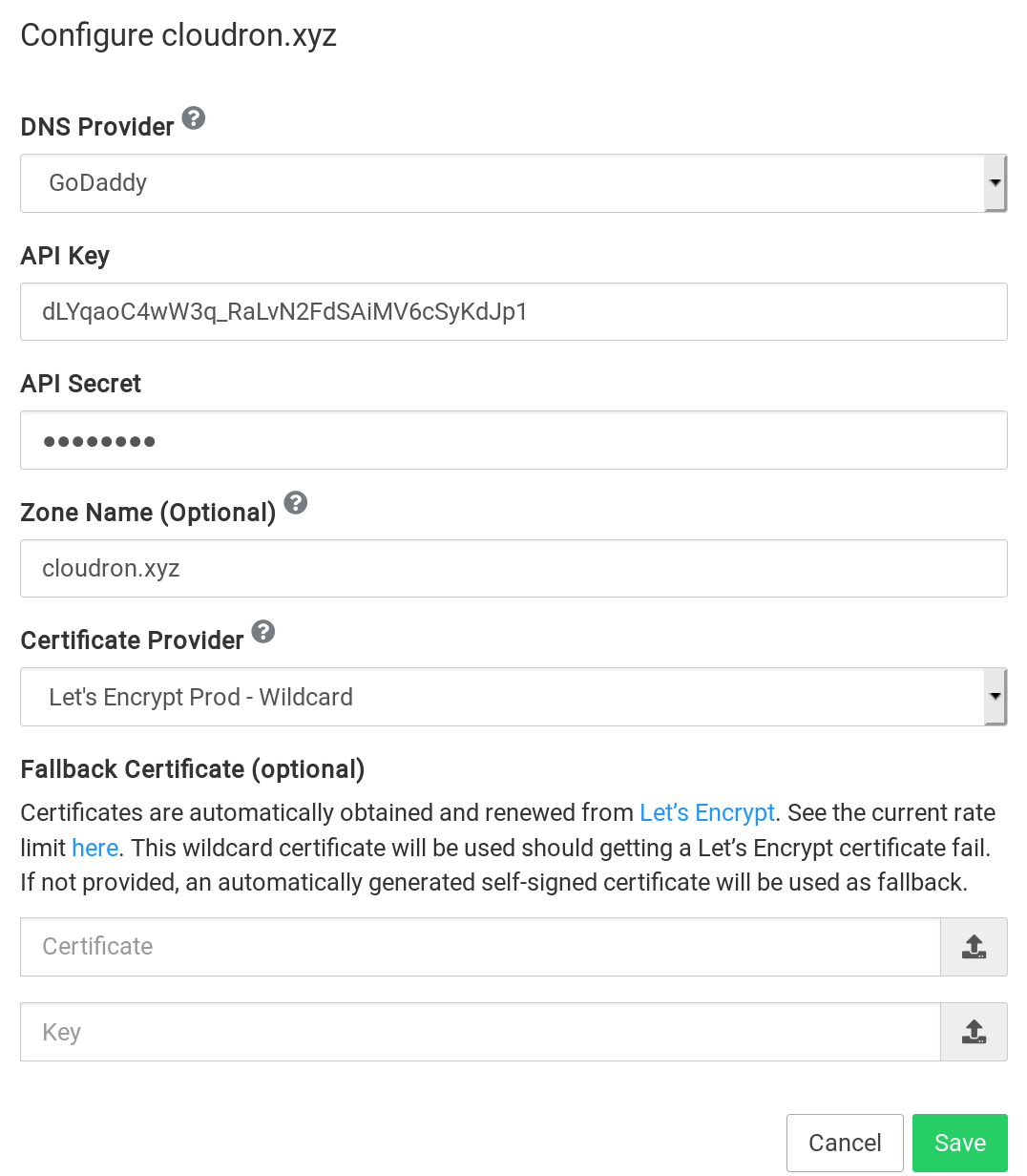
You can upload a certificate chain by simply appending all the intermediate certs in the same cert file.
App certificate
Custom certificates can also be set for each installed application using the REST API.
This can be used to set an Extended Validation (EV) certificate for an app. For example,
assuming we have the PEM encoded files cert.pem and key.pem:
# first encode the newlines to send as JSON
key=$(perl -pe 's/\n/\\\n/' key.pem)
cert=$(perl -pe 's/\n/\\n/' cert.pem)
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"cert\": \"${cert}\", \"key\": \"${key}\" }" https://my.cloudron.xyz/api/v1/apps/5555f553-96ad-46c9-ba42-13d08ecb86a0/configure?access_token=3f1e6d8e5ece3f3dbdefd88679fdd270b00223b58ce6781990cf95e444b7c7f3
In the example above, my.example.com is the Cloudron domain. 5555f553-96ad-46c9-ba42-13d08ecb86a0 is the app id obtained from the Updates section of the app. API tokens can be created in the profile view.
You can upload a certificate chain by simply appending all the intermediate certs in the same cert file.
Certificate transparency
Let's Encrypt participates in Certificate transparency. This means that your apps and subdomains are discoverable via the Certificate transparency project (crt.sh and Google's website). Some hackers take advantage of this to hack web applications before they are in installed.
For this reason, we recommend that you use Wildcard certificates. When using Wildcard certificates, the subdomain information is not 'leaked'. Note that Let's Encrypt only allows obtaining wildcard certificates using DNS automation. Cloudron will default to obtaining wildcard certificates when using one of the programmatic DNS API providers.
Renewal
Automatic renewal
Cloudron attempts to start renewing certificates automatically 1 month before expiry of the certificate. If renewal fails, a notification email will be sent to the Cloudron administrators. When the certificate expires, Cloudron will start using fallback certificates for the app.
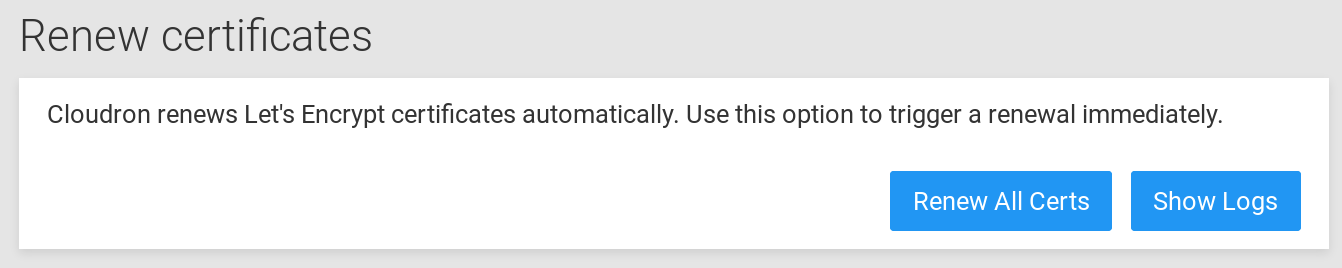
Manual renewal
To instantly trigger renewal of Let's encrypt certificate, click the Renew All button on the domains page.
Revokation
Cloudron does not revoke certificates when an app is uninstalled. Instead, it retains the
certificate, so that it can be reused if another app is installed in the same
subdomain. This allows you to install apps for testing in the same location, say test,
and not have to worry about running over the Let's Encrypt rate limit.
CAA records
Starting Sep 2017, Let's Encrypt will check for CAA records to validate if the domain owner
has authorized the CA to issue certificates for the domain. For this reason, make sure that
either the CAA record for the domain is empty
OR setup a CAA record allowing letsencrypt.org.